What are the pros and cons of leasing vs buying a car? – When it comes to acquiring a set of wheels, the age-old debate of leasing versus buying rages on. Both options offer distinct advantages and drawbacks, and the optimal choice hinges on your individual circumstances and preferences. Let’s delve into the intricacies of each to help you make an informed decision.
Financial Considerations
Understanding the financial implications is crucial when deciding between leasing and buying a car. Both options have distinct upfront costs, monthly payments, and long-term financial obligations.
Upfront Costs
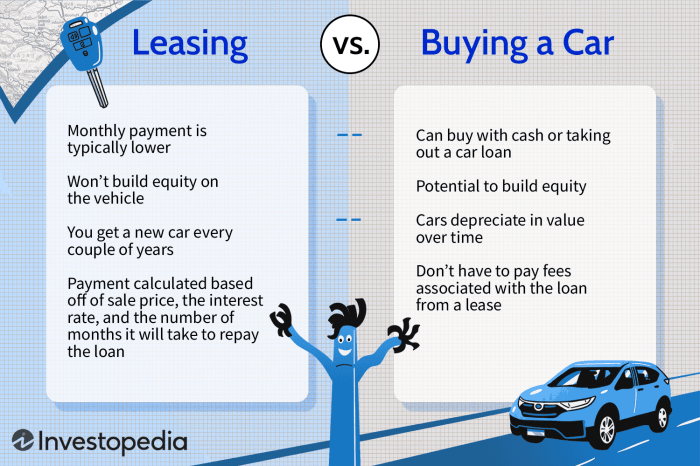
- Leasing:Typically requires a smaller down payment or security deposit compared to buying.
- Buying:Involves a larger down payment, often 20% or more of the vehicle’s price.
Monthly Payments
Monthly lease payments are generally lower than loan payments for buying a car. This is because you’re only paying for the depreciation of the vehicle during the lease term, not the entire cost.
Long-Term Costs
- Leasing:Over the long term, leasing can be more expensive than buying, as you do not own the vehicle at the end of the lease.
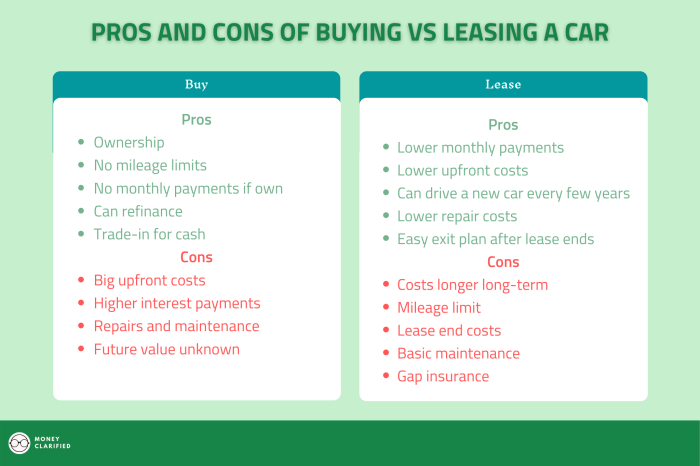
- Buying:While monthly payments may be higher, buying a car allows you to build equity in the vehicle and potentially sell it for a profit in the future.
Lease Terms
Lease terms can significantly impact your financial obligations. Factors to consider include the lease length (usually 24, 36, or 48 months), mileage limits, and early termination fees.
Ownership and Equity
When you lease a car, you don’t own it. You’re essentially renting it for a set period of time, typically 2-4 years. At the end of the lease, you can either return the car to the dealership or purchase it.
When you buy a car, you own it outright. You can keep it as long as you want, sell it, or trade it in.Building equity is another important consideration. Equity is the difference between what you owe on your car and its current market value.
When you lease a car, you’re not building any equity. However, when you buy a car, you’re building equity every time you make a payment. This can be a valuable asset, especially if you plan on selling or trading in your car down the road.If you’re considering leasing a car, it’s important to be aware of the potential drawbacks.
One of the biggest drawbacks is that you don’t own the car at the end of the lease. This means that you don’t have any equity in the car, and you’ll have to start over if you want to get a new car.
Additionally, leases often come with mileage restrictions, and you could face penalties if you exceed those limits.
Purchasing a Leased Vehicle
If you’re nearing the end of your lease and you’re interested in purchasing the car, you have a few options. You can negotiate a purchase price with the dealership, or you can finance the purchase through a bank or credit union.
If you decide to finance the purchase, you’ll need to factor in the cost of the loan, as well as the interest rate.
Flexibility and Customization

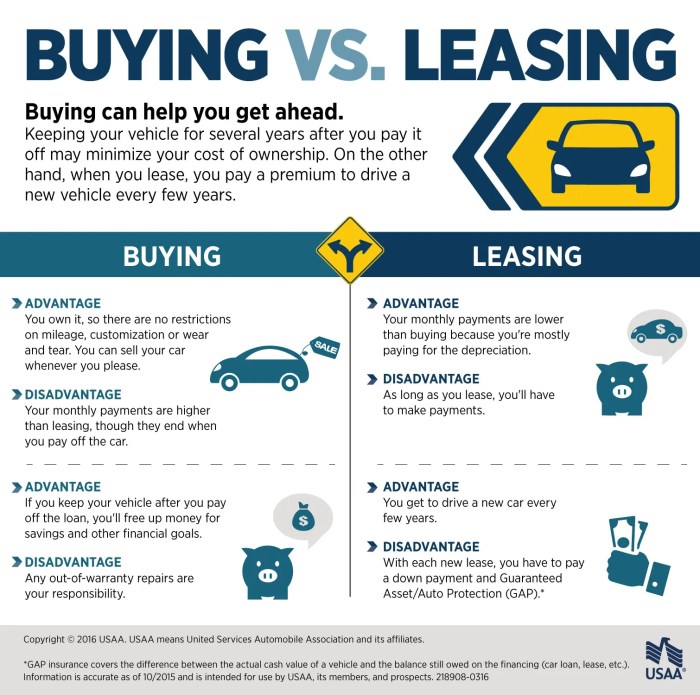
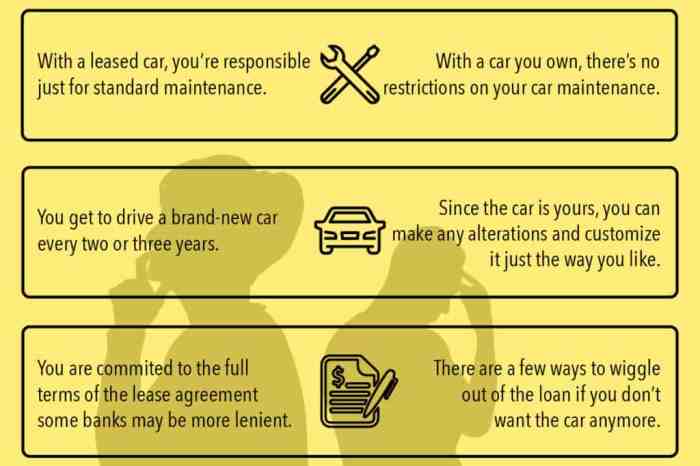
Leasing and buying differ significantly in terms of flexibility and customization options. When leasing, you’re typically limited to the vehicles offered by the leasing company, which may not align with your specific preferences or needs. In contrast, buying a car gives you complete freedom to choose any vehicle that meets your requirements.
Customizing a Leased Vehicle
Customizing a leased vehicle is generally restricted due to contractual agreements. Modifications that alter the vehicle’s appearance or performance may violate the lease terms. Additionally, any unauthorized changes can result in penalties or fees at the end of the lease period.
Maintenance and Repairs
Leasing a car typically involves different responsibilities for maintenance and repairs compared to buying one. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision about whether leasing or buying is right for you.
Responsibilities under a Lease Agreement
In a lease agreement, the lessee (the person leasing the car) is usually responsible for routine maintenance, such as oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections. However, major repairs, such as engine or transmission problems, are typically covered by the lessor (the company or dealership that owns the car).
It’s important to check the specific terms of your lease agreement to understand your responsibilities.
Potential Costs and Coverage
The potential costs and coverage for maintenance and repairs can vary depending on whether you lease or buy a car. With a lease, you may have lower monthly payments, but you may also have to pay for certain repairs that would be covered under a warranty if you bought the car.
On the other hand, buying a car typically means higher monthly payments, but you will also have more control over maintenance and repairs, and you may be able to save money in the long run by doing some of the work yourself.
Excessive Wear and Tear
When you lease a car, you are expected to return it in good condition at the end of the lease term. If the car has excessive wear and tear beyond normal use, you may be charged additional fees. These fees can vary depending on the severity of the damage and the terms of your lease agreement.
Mileage Limits and Restrictions
When leasing a car, you typically have a set mileage limit per year. Exceeding this limit can result in penalties.
Mileage limits vary depending on the lease agreement and can range from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year. If you exceed the limit, you may be charged a per-mile penalty, which can add up quickly.
Impact on Driving Habits and Flexibility
Mileage limits can impact your driving habits and flexibility. If you drive more than the allotted miles, you may need to adjust your driving habits or risk incurring penalties.
For example, if you have a 12,000-mile-per-year lease and you drive 15,000 miles, you may be charged a penalty of 15 cents per mile for the additional 3,000 miles. This would result in a penalty of $450.
Early Termination
When entering a lease agreement, it’s crucial to understand the terms and conditions surrounding early termination. Both leasing and buying a car involve different implications for terminating the contract before its expiration.
Leasing contracts typically include specific clauses outlining the penalties and fees associated with early termination. These can vary depending on the lease terms and the remaining duration of the lease. Generally, early termination fees for leases are higher than those for buying a car.
This is because the lessor (the company you lease the car from) has to recover the remaining value of the car and any lost rental income.
Circumstances Justifying Early Termination
While early termination is generally discouraged due to potential fees, there may be certain circumstances that justify it. These include:
- Job loss or relocation
- Significant financial hardship
- Health issues that prevent you from driving
- Total loss or damage to the leased vehicle
- Military deployment
It’s important to carefully consider the potential costs and consequences of early termination before making a decision. Consulting with a financial advisor or attorney can provide valuable guidance in such situations.
Tax Implications
Leasing and buying a car have different tax implications that can affect your financial decision.
Tax Deductions and Credits
* Leasing:Lease payments are generally not tax-deductible for personal use. However, businesses can deduct a portion of their lease payments as a business expense.
Buying
Loan interest on auto loans can be tax-deductible for personal use, up to a certain amount. Additionally, you may qualify for tax credits if you purchase an electric or hybrid vehicle.
Sales Tax
* Leasing:You typically pay sales tax on the monthly lease payments rather than the full purchase price. This can result in lower sales tax payments over the lease term.
Buying
You pay sales tax on the full purchase price of the vehicle upfront. This can be a significant expense, especially for higher-priced vehicles.
Early Lease Termination
* Early Lease Termination:If you terminate your lease early, you may face significant penalties and fees. These penalties can be taxable as income.
Lifestyle Considerations

Leasing or buying a car aligns with different lifestyles based on factors like driving habits, financial situation, and personal preferences.For frequent drivers or those who prefer driving newer vehicles, leasing offers convenience and flexibility. Lease terms typically range from 24 to 48 months, allowing drivers to upgrade to a newer model more often.
Additionally, lease payments are often lower than loan payments for a similar vehicle.On the other hand, buying a car provides the benefits of ownership, including long-term stability and customization. Owners can build equity in their vehicle, customize it to their liking, and drive it for as long as they want without mileage restrictions.
However, loan payments are typically higher than lease payments, and owners are responsible for all maintenance and repairs.
Convenience and Flexibility of Leasing
Leasing offers convenience and flexibility for those who:
- Drive frequently and prefer to have a newer vehicle every few years.
- Want lower monthly payments compared to buying a similar vehicle.
- Value the option to upgrade to a newer model at the end of the lease term.
- Do not want to deal with the hassle of selling or trading in a vehicle.
Credit Requirements
Leasing and buying a car require different credit qualifications. Understanding these requirements can help you make an informed decision.
Leasing
- Typically requires a higher credit score than buying.
- Lenders want to ensure you’re a low risk and will make payments on time.
- A good credit score can lead to lower interest rates and more favorable lease terms.
Buying
- Generally requires a lower credit score than leasing.
- Lenders may be more lenient as you’re building equity in the vehicle.
- However, a higher credit score can still secure better interest rates and loan terms.
Alternative Financing Options
If you have a lower credit score, consider these alternatives:
- Co-signer:Have someone with good credit co-sign your loan.
- Subprime loan:These loans have higher interest rates but can be an option for those with lower scores.
- Lease-to-own programs:Allow you to lease a car with the option to buy it at the end of the lease.
Resale Value: What Are The Pros And Cons Of Leasing Vs Buying A Car?
Resale value is an important consideration when deciding whether to lease or buy a car. Several factors affect the resale value of a vehicle, including its make, model, year, mileage, condition, and market demand.
Depreciation
Depreciation is the loss of value that a vehicle experiences over time. Leased vehicles typically depreciate less than purchased vehicles because the lessee does not own the vehicle and is only responsible for the depreciation that occurs during the lease term.
Mileage, What are the pros and cons of leasing vs buying a car?
Mileage is a significant factor that affects resale value. Vehicles with higher mileage are generally worth less than vehicles with lower mileage. This is because high mileage can indicate that the vehicle has been driven more often and may have experienced more wear and tear.
Condition
The condition of a vehicle also affects its resale value. Vehicles that are in good condition are worth more than vehicles that are in poor condition. This includes the vehicle’s exterior, interior, and mechanical components.
Market Demand
Market demand can also affect resale value. Vehicles that are in high demand are worth more than vehicles that are not in high demand. This is because there are more potential buyers for vehicles that are in high demand, which drives up the price.
Environmental Considerations
Leasing vs. buying a car has different environmental implications. Leasing generally leads to lower emissions and reduced waste compared to buying.
When you lease a car, you’re essentially renting it for a period of time. At the end of the lease, you can return the car to the dealership or buy it outright. This means that you’re not responsible for the car’s long-term maintenance or disposal, which can reduce your environmental impact.
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
Leasing can be a great option if you’re interested in driving an electric or hybrid vehicle. These vehicles produce fewer emissions than gasoline-powered cars, and leasing can help you save money on fuel costs.
Summary
Ultimately, the decision between leasing and buying boils down to your unique needs and financial situation. By carefully considering the factors discussed, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your lifestyle and long-term goals. Whether you prioritize flexibility, ownership, or cost-effectiveness, there’s an option that suits your automotive aspirations.
FAQ Explained
What’s the main difference between leasing and buying a car?
When you lease, you’re essentially renting the car for a fixed period, typically 2-4 years. At the end of the lease, you can return the car or purchase it. When you buy a car, you own it outright and are responsible for all maintenance and repairs.
Which option is more affordable?
Leasing is often more affordable than buying, especially in the short term. Monthly lease payments are typically lower than loan payments for a comparable car. However, over the long term, buying a car can be more cost-effective if you plan to keep it for many years.
What are the mileage restrictions on leased cars?
Leased cars typically have mileage restrictions, which can range from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year. If you exceed the mileage limit, you may have to pay a penalty fee.
Can I customize a leased car?
Yes, but it’s important to get approval from the leasing company before making any modifications. Unauthorized modifications can result in penalties at the end of the lease.