What is the difference between a hybrid and an electric car? In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences between these two eco-friendly options to help you make an informed decision about your next car purchase.
Hybrid cars combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor, while electric cars run solely on electricity stored in a battery. This difference has a significant impact on fuel consumption, emissions, performance, and cost.
Overview of Hybrid Cars
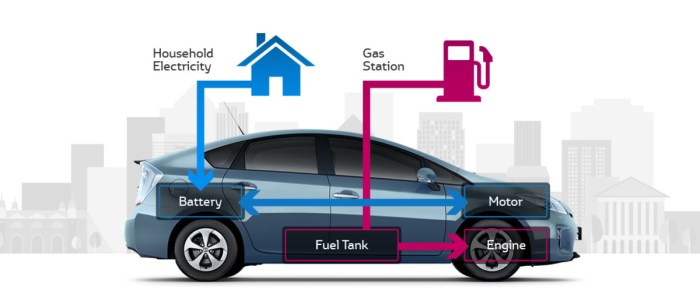
Hybrid cars combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor and battery to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The ICE powers the car at higher speeds, while the electric motor assists at lower speeds or during acceleration.
Types of Hybrid Systems
- Parallel Hybrid:The most common type, with both the ICE and electric motor connected to the transmission.
- Series Hybrid:The ICE generates electricity that powers the electric motor, which drives the wheels.
- Plug-in Hybrid:Has a larger battery that can be charged externally, allowing for longer electric-only driving.
Overview of Electric Cars
Electric cars, often referred to as EVs, are powered exclusively by electric motors, drawing energy from high-voltage battery packs. Unlike hybrid cars, they have no internal combustion engine, making them emission-free during operation.
Electric Motors
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, powering the car’s wheels. They offer instant torque, providing smooth and responsive acceleration. Electric motors are also highly efficient, utilizing energy more effectively than internal combustion engines.
Battery Packs
Battery packs store the electrical energy used to power the electric motor. They consist of multiple individual battery cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in EVs due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
Charging Methods
Electric cars can be charged using various methods, each with its own implications:
Level 1 Charging (120V)
Uses a standard household outlet, providing slow charging speeds suitable for overnight charging at home.
Level 2 Charging (240V)
Employs a dedicated charging station that provides faster charging than Level 1, often used for home or public charging.
DC Fast Charging
Utilizes high-voltage direct current to rapidly charge the battery, typically found at public charging stations, enabling a significant range extension in a short amount of time.
Fuel Consumption and Efficiency
Hybrid and electric cars offer significant differences in fuel consumption and efficiency, impacting both your wallet and the environment.
Hybrid cars combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, allowing them to operate on both fuel and electricity. This combination typically results in improved fuel economy compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Fuel Economy
Hybrid cars typically achieve higher fuel economy than conventional cars due to their ability to switch between electric and gasoline power. According to the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the average fuel economy of hybrid cars is around 50 miles per gallon (mpg), compared to around 25 mpg for gasoline-powered vehicles.
Range
Electric cars, on the other hand, rely solely on electricity to power their motors. This means they have a limited range, which varies depending on the size of the battery and driving conditions.
The average range of electric cars is between 100 and 200 miles on a single charge. However, factors such as speed, acceleration, and temperature can significantly impact the range.
Driving Conditions
Both hybrid and electric cars are affected by driving conditions, but in different ways. Hybrid cars can benefit from regenerative braking, which captures energy during deceleration and stores it in the battery, improving fuel efficiency.
Electric cars, on the other hand, are more sensitive to factors such as temperature and terrain. Cold temperatures can reduce battery capacity, while driving in hilly areas or at high speeds can increase energy consumption.
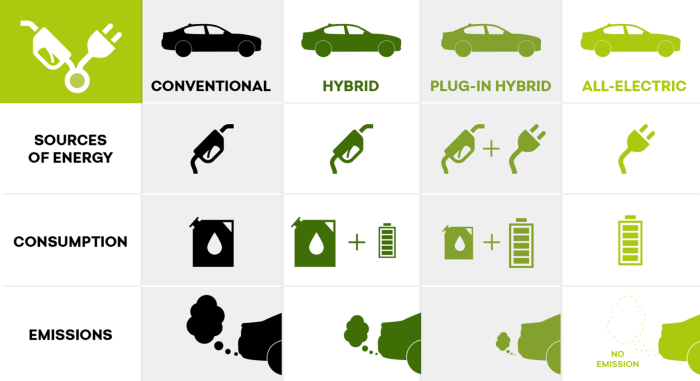
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Hybrid and electric cars have distinct emissions profiles and environmental impacts. Hybrid cars still use gasoline, but they produce fewer emissions than conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. Electric cars, on the other hand, produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them more environmentally friendly.
Life-Cycle Emissions
The environmental impact of a vehicle extends beyond its tailpipe emissions. The production, use, and disposal of the vehicle all contribute to its life-cycle emissions. Electric cars have higher upfront emissions due to the production of their batteries, but they make up for it with lower emissions during use.
Hybrid cars have lower life-cycle emissions than gasoline-powered vehicles but higher than electric cars.
Environmental Benefits
Both hybrid and electric cars offer environmental benefits compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. Hybrid cars reduce fuel consumption and emissions, while electric cars eliminate tailpipe emissions altogether. This can lead to improved air quality, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and a cleaner environment.
Challenges
The widespread adoption of hybrid and electric cars faces several challenges. The high cost of electric cars can be a barrier for many consumers. Additionally, the limited driving range of electric cars can be a concern for some drivers. Infrastructure challenges, such as the availability of charging stations, also need to be addressed to support the growing number of electric vehicles on the road.
Performance and Driving Experience
Hybrid and electric cars offer distinct driving experiences due to their different powertrains. Hybrid cars combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor, providing both fuel efficiency and enhanced performance. Electric cars, on the other hand, rely solely on electric motors, offering instant acceleration and a smooth, quiet ride.
Acceleration and Speed
Electric cars typically have quicker acceleration than hybrid cars, especially from a standstill. Electric motors provide instant torque, eliminating the need for a transmission and resulting in a more responsive driving experience. Hybrid cars, while not as quick off the line, can still offer impressive acceleration when both the gasoline engine and electric motor work together.
Handling
The placement of electric motors in electric cars often results in a lower center of gravity, contributing to improved handling and stability. Electric cars also benefit from regenerative braking, which uses the electric motor to slow the car and recovers energy in the process.
This can provide a more controlled and efficient driving experience.
Smoothness and Responsiveness, What is the difference between a hybrid and an electric car?
Electric cars offer a smoother and more responsive driving experience than hybrid cars. The lack of a traditional transmission eliminates gear changes, resulting in a seamless and uninterrupted ride. Electric motors also provide instant power delivery, making the car more responsive to driver inputs.
Noise Levels
Electric cars are significantly quieter than hybrid cars, especially at low speeds. The absence of a gasoline engine means that electric cars produce minimal noise, creating a more peaceful and relaxing driving environment. Hybrid cars, while quieter than conventional gasoline-powered vehicles, still have some engine noise when operating in gasoline mode.
Charging Infrastructure and Availability

The availability of charging infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric cars. Currently, the charging infrastructure for electric cars is rapidly expanding, but there are still challenges and opportunities to improve its coverage and accessibility.
One of the key challenges is the uneven distribution of charging stations. While some areas have a dense network of charging stations, others have limited or no access to charging infrastructure. This can make it difficult for electric car owners to travel long distances or to find a charging station when they need it.
Government Initiatives
Governments around the world are playing a significant role in expanding charging infrastructure. They are providing incentives for the installation of charging stations and working with private companies to develop and deploy charging networks. For example, the US government has set a goal of having 500,000 public charging stations by 2030.
Private Sector Investment
The private sector is also investing heavily in charging infrastructure. Companies such as Tesla, ChargePoint, and Electrify America are building and operating charging stations across the country. These companies are working to make charging convenient and accessible for electric car owners.
The expansion of charging infrastructure is having a positive impact on the adoption of electric cars. As more charging stations become available, it becomes easier for people to own and operate electric cars. This is leading to increased sales of electric cars and a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Future Trends and Innovations
The hybrid and electric car industry is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging all the time. These advancements have the potential to improve efficiency, performance, and affordability, making hybrid and electric vehicles even more appealing to consumers.One of the most promising trends is the development of more efficient batteries.
Batteries are the key component of electric vehicles, and their performance directly impacts the vehicle’s range and overall efficiency. Researchers are working on new battery technologies that can store more energy, charge faster, and last longer. These improvements will make electric vehicles more practical and appealing to a wider range of consumers.Another important trend is the development of new charging technologies.
Currently, most electric vehicles are charged using a standard household outlet, which can take several hours. New charging technologies, such as wireless charging and fast charging, can significantly reduce charging times, making electric vehicles more convenient to use.In addition to battery and charging technology, there are also a number of other innovations that are expected to impact the future of hybrid and electric vehicles.
These include:
- Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), which can help to improve safety and reduce the risk of accidents.
- Autonomous driving technology, which has the potential to revolutionize the way we travel.
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, which allows electric vehicles to store energy and then discharge it back to the grid during peak demand periods.
These are just a few of the emerging trends and innovations that are expected to shape the future of hybrid and electric vehicles. As these technologies continue to develop, hybrid and electric vehicles will become more efficient, affordable, and convenient, making them an increasingly attractive option for consumers.
Closing Summary: What Is The Difference Between A Hybrid And An Electric Car?

Ultimately, the best choice for you depends on your individual needs and preferences. If you’re looking for a fuel-efficient option that’s still affordable and easy to maintain, a hybrid car may be a good fit. If you’re committed to zero emissions and are willing to invest in a more advanced technology, an electric car could be the right choice.
FAQ Insights
Q: Which is more fuel-efficient, a hybrid or an electric car?
A: Electric cars are more fuel-efficient than hybrid cars, as they don’t use any gasoline.
Q: Which produces fewer emissions, a hybrid or an electric car?
A: Electric cars produce zero emissions, while hybrid cars produce some emissions when running on gasoline.
Q: Which is more expensive to purchase, a hybrid or an electric car?
A: Electric cars are typically more expensive to purchase than hybrid cars, but they may be eligible for government incentives.